
Share
Do gurgling lung sounds mean an emergency?
Gurgling lung sounds often indicate fluid or secretions in the airways and can signal an urgent problem when paired with respiratory distress. In acute care, recognizing gurgling lung sounds quickly helps clinicians decide when suctioning, airway support, or escalation is needed to prevent deterioration.
Gurgling Lung Sounds in Acute Care: When to Act
⏱ 7 min read · Gurgling lung sounds can be subtle, intermittent, or masked by background noise—yet they often carry critical meaning. In fast-moving clinical environments, knowing when these sounds require immediate action can change outcomes. This guide breaks down what you’re hearing, why it matters, and how modern listening tools help clinicians act with confidence.
Which patients are most at risk when gurgling lung sounds are missed? Read on to see how timing, clarity, and context guide safer decisions.

Gurgling lung sounds during assessment can signal airway fluid—clear listening supports faster decisions. 💡 See it in action
What are gurgling lung sounds?
Gurgling lung sounds are low-pitched, bubbling noises heard during inspiration or expiration. They usually suggest air passing through fluid, mucus, or secretions in larger airways. In acute care, these sounds demand attention because they can rapidly worsen if the airway becomes compromised.
How they typically present
- Wet, bubbling quality that may change after coughing
- Often louder over central airways
- May coexist with crackles or rhonchi
- Can fluctuate with patient position
Common causes in acute care
Understanding context is essential for unclear lung sounds diagnosis. Gurgling can stem from benign, reversible issues—or signal impending failure.
- Excess secretions: Common in pneumonia or bronchitis
- Pulmonary edema: Fluid overload or heart failure
- Aspiration: Vomit or oral secretions entering airways
- Reduced cough reflex: Sedation or neurologic impairment
When should clinicians act immediately?
Gurgling lung sounds require prompt action when paired with clinical decline. Waiting for imaging can delay lifesaving care.
Red flags that demand escalation
- Increasing work of breathing or oxygen needs
- Altered mental status
- Inability to clear secretions
- Rapid progression over minutes to hours
Early intervention—such as suctioning, airway positioning, or respiratory support—often prevents intubation.
Why unclear lung sounds diagnosis is so common
Noisy clinical auscultation is a daily reality in emergency rooms and ICUs. Alarms, conversations, and equipment hum make subtle sounds easy to miss.
Key challenges clinicians face
- Background noise masking low-frequency sounds
- Time pressure during rapid assessments
- Patient movement or agitation
- Variable clinician hearing sensitivity
These factors contribute to delayed recognition and inconsistent documentation.
How clearer listening improves decisions
Electronic stethoscope noise reduction helps separate true lung sounds from ambient interference. By amplifying clinically relevant frequencies, clinicians gain confidence in what they hear.
Tools designed for intelligent noise reduction function like a precision filter—reducing background clutter while preserving diagnostic detail.
Benefits clinicians report
- Faster differentiation between gurgling and crackles
- Improved handoff communication
- Reduced repeat assessments
- Greater confidence during night shifts
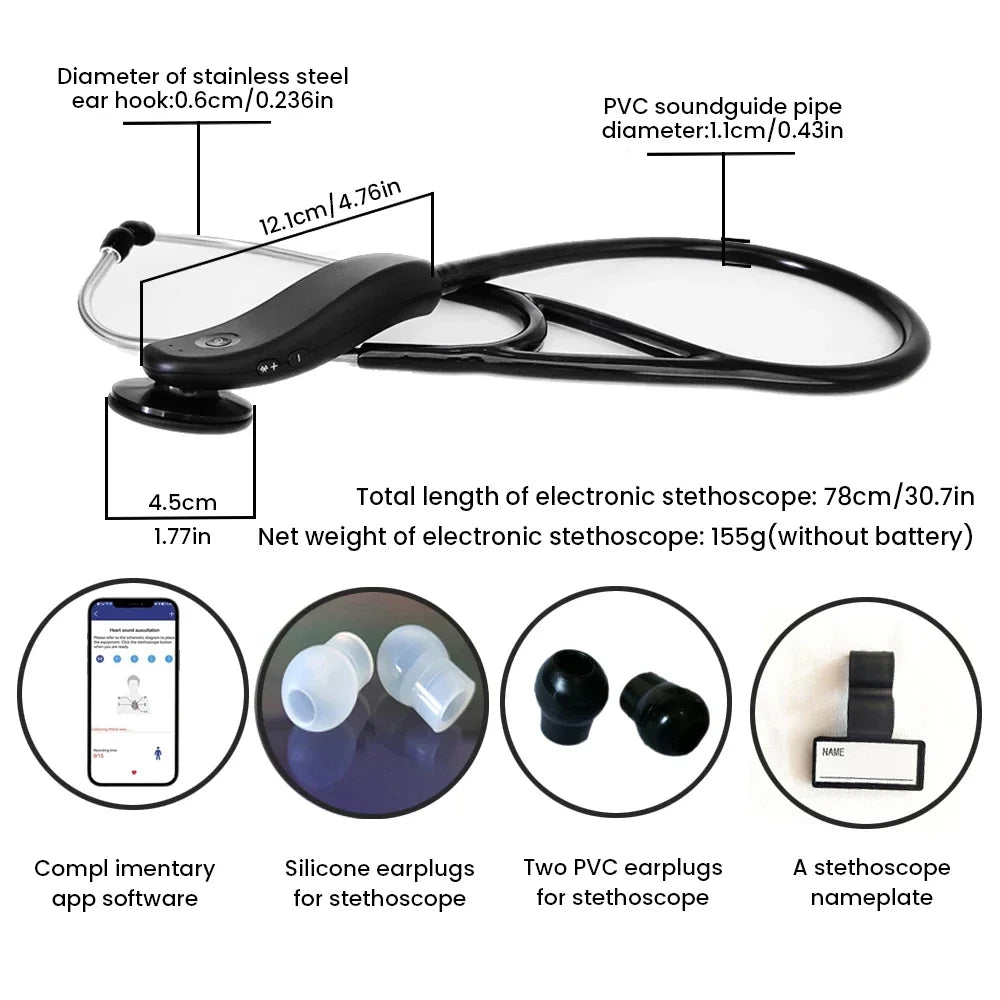
Noisy clinical auscultation becomes clearer with electronic stethoscope noise reduction. 💡 See it in action
Workflow benefits in noisy settings
In busy units, time saved matters. Amplified stethoscope technology supports quicker assessments without repeating exams.
| Traditional Listening | Enhanced Listening |
|---|---|
| Sound masked by noise | Focused lung sound clarity |
| Frequent reassessment | Faster initial decisions |
| Variable interpretation | More consistent findings |
These gains align with broader safety goals often discussed within Health & Safety initiatives.
Real-world clinical stories
“During a crowded night shift, I caught subtle gurgling early and suctioned before the patient desaturated,” shared an ICU nurse. “Clearer sound made the difference.”
Another clinician noted improved teaching moments for residents when sounds were easier to distinguish.

Clearer detection of gurgling lung sounds supports faster escalation decisions. 💡 See it in action
Supporting clinician focus and wellness
Fatigue and sensory overload are real. Reducing listening strain can support concentration and reduce errors—an often-overlooked aspect of Beauty & Wellness for healthcare professionals.
Quick FAQs
Can gurgling lung sounds resolve on their own?
Sometimes, especially after coughing or repositioning. Persistent gurgling, however, should prompt evaluation for fluid or secretion buildup.
Are gurgling sounds always abnormal?
They are usually abnormal in adults, particularly in acute settings, and warrant clinical correlation.
Does better amplification change outcomes?
Clearer sound supports faster recognition and earlier intervention, which can prevent deterioration in vulnerable patients.
Pillar Article: Heart Lung Sounds for Different Patients: What to Listen For
Other Related Articles:
Explore More:












